IDE64
| IDE64 | |
 | |
| Type: | EIDE-Interface |
| Producer: | Tomas Pribyl, Jan Vorlicek, Josef Soucek |
| Price: | 105 € |
| Released: | 1994 |
| Discontinued: | |
| Processor: | |
| Memory: | |
| OS: | |
| Info: | differents versions; latest version 4.1 |
The IDE64 is an ATA/ATAPI interface cartridge for the C64 and the C128 (in C64 mode). The latest version (v4.1) was released in March 2009.
Origins[edit | edit source]

The IDE64 was originally developed in 1994 by Tomas Pribyl and Jan Vorlicek. The current custodian is Josef Soucek.
Features[edit | edit source]

The IDE64 has the following features:
- Real-time data transfer between C64/C128 and a PC.
- Storage of setup settings.
- Timestamping of files with a real-time clock.
- Compatibility with GEOS and WINGs.
- Access to mass storage devices (up to 3 simultaneously) such as:
- External hard disk.
- CDROM.
- DVD (Digital Versatile Disk).
- Zip drive.
- LS-120 (Laser Servo Drive).
- CF (CompactFlash).
Software[edit | edit source]
The IDE64 is loaded with the following software:
- IDE64-DOS V.90 firmware, switchable between C64 Standard and C64 SuperCPU (from v3.4+,) and includes support for.
- CMOS setup
- Partitions.
- Relative files.
- Streaming HiRes video at 25 fps.
- BASIC extension.
- Quick charger.
- File manager.
- Machine language monitor.
Hardware[edit | edit source]
The IDE64 consists of a PCBA (components in Table 1) which connects to the expansion port.
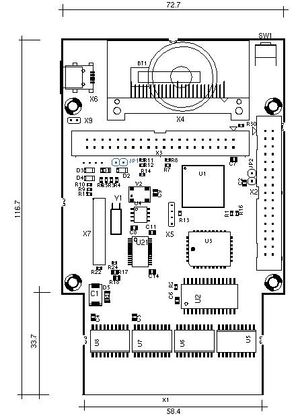
| Table 1 - IDE64 Hardware Components | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Designator | Code | Component | Added |
| U1 | M4A5-128/64 | 28 KByte RAM internal buffer | (from v2.1) |
| U2 | 62V256 | 32 KByte 8-bit low power and low Vcc CMOS static RAM | |
| U3 | 29C010A | 128 KByte 5-Volt CMOS EEPROM for firmware | (from v3.4+) |
| U4 | DS1302 | Trickle-Charge Timekeeping IC | (from v1.1) |
| U5 | 74HCT245 | 3-State Octal Bus Transceiver | (from v4.1) |
| U6 | 74HCT541 | 3-State Octal Line Driver | (from v4.1) |
| U7 | 74HCT541 | 3-State Octal Line Driver | (from v4.1) |
| U8 | 74HCT541 | 3-State Octal Line Driver | (from v4.1) |
| U21 | FT245RL | Single IC USB to parallel FIFO Bi-directional Data Transfer Interface | (from v4.1) |
| JP1 | Jumper for updating the EEPROM with a newer IDE DOS version | (from v1.1) | |
| JP2 | Jumper for swapping address range $DE00-$DE0F with $DE10-$DDE1F | ||
| BT1 | Socket for button cell battery CR2032, Li. 3 V, 200 mA | (from v1.1) | |
| SW1 | Reset Button | (from v1.1) | |
| X2 | 34-pin ShortBus | (from v2.1) | |
| X3 | 40-pin IDE bus | (from v1.1) | |
| X4 | CF socket without external power supply requirement | (from v4.1) | |
| X6 | USB 1.1/2.0 Mini-B device port | (from v4.1) | |
| X7 | 22-pin general expansion Amiga clock port | ||
| L1 | LED (Green) indicating cartridge connection | (from v3.1) | |
| L2 | LED (Red) indicating IDE bus activity | (from v4.1) | |
Version History[edit | edit source]
| Table 2 - Revisions of The IDE64 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Version | Release Date | Remarks | PCBA |
| v4.1 | March 2009 (Pre-release August 2009) | The hardware was redesigned to use surface-mounted parts and a more up-to-date ispMACHCPLD, which resulted in a much shorter board. An USB serial FIFO chip was added for fast PCLink connections. An Amiga clock-port was added for connecting additional devices. The CF socket is separated from the parallel ATA port; which is more compatible to strange CF cards. The I/O interface was changed to support 128 KByte OS and was tweaked for slightly faster data transfer speeds. The CF socket needs no additional power supply, and has a low power consumption (approx. 140 mA). Standard ATA hard disk drives and CD/DVD ROMs, with or without a CF socket option, can now be used. | 
|
| v3.4+ | 2005 | The EEPROM was upgraded to 128 KByte. The OS was now switchable between standard C64 and SuperCPU; this solved the reflashing problem for those with SuperCPU-equipped systems. | |
| v3.4 | 2004 | A CF socket was added. | 
|
| v3.1 | 2001 | The expansion port pass-through was removed. | 
|
| v2.1 | 1999 | The logic was combined onto a single ispLSI PLD. The OS became upgradable on a 32 KByte EEPROM. The buffer was increased to 28 KByte. The ShortBus connector was added; originally designed for LCD displays and SSD LEDs. SuperCPU compatibility was included. | 
|
| v1.1 | December 1997 | The logic was fitted into 2 ispLSI PLDs. The OS was burned into a 32 KByte EEPROM. The buffer consisted of 16 KByte RAM. Timestamping ans settings were enabled by a DS1302 real-time clock and additional battery. Peripherals were added by a parallel ATA connector. An expansion port pass-through allowed other cartridges to be attached. | 
|
ShortBus Expansions[edit | edit source]
Peripherals that are known to work with the IDE64 are:
- ETH64. A 10 Mbit LAN91C96-based Ethernet card.
- DUART. A XR68C681-based dual RS-232 card.
- RR-Net. A CS8900a-based networking card.
- DigiMAX. A MAX506-based 4 channel 8-bit digital-to-analogue converter card.
- ETFE. A CS8900-based networking card.
Expanded BASIC[edit | edit source]

The IDE64 has 19 new BASIC commands.
Functions keys[edit | edit source]
The normal activated functions keys have this function:
- F1
^!*,p chr$(13)- LOAD"!*,p" and RUN, CHR$(13) for hitting RETURN - F2
%:* chr$(13)- LOAD":*,dr,1" - F3
@$ chr$(13)- List directory without losing data - F4
@$*=p- List only PRG files of a directory - F5
lI chr$(13)- LIST: List a BASIC program - F6
ll chr$(13)- List directory in detail - F7
rU chr$(13)- RUN: Starts a BASIC program - F8
mA chr$(13)- MANAGER: Start the IDE64 file manager
File manager[edit | edit source]
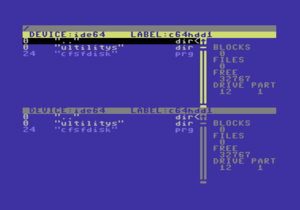
The file manager can start with the command MAN. It supports until 4 disk drives (with device numbers 8-11), 2 IDE devices (12,13), PC-Link (14) and a CF-flash card (15). It looks like the Norton Commander. It can shown max. 510 files of a directory.
The menu is activated with the key C= and controls by the cursor keys, RETURN and RUN/STOP .
For toggling between the windows is used the key CTRL -Taste.
Following keys are also used:
- F1 Page return
- F2 First page
- F7 Page forward
- F8 End of page
- 1 or / reread directory
- 4 Start of file viewer or enter
/viewer - 5 Copy file
- 6 Rename file
- 7 Create (sub)directory
- 8 Delete file
- + Select whole directory
- - Deselect whole directory
- ← Exit the file manager
New BASIC Errors[edit | edit source]
(Only in IDEDOS v.8x, IDEDOS v.9 hasn't no new BASIC errors)
- ?HD ERROR
- ?DISK FULL ERROR
- ?LAST DIR SECTOR ERROR
- ?FILE IS NOT DIR ERROR
- ?WRITE PROTECT ERROR
- ?FILE TYPE ERROR
- ?BAM ERROR
- ?DIR IS NOT EMPTY ERROR
- ?FILE DID EXIST ERROR
Machine Code Monitor[edit | edit source]
The key combinations C= +RESTORE start the monitor for coding assembler programs.
- A Assemby
- B Memory-Switch
- C Compare
- D Disassembly
- E Edit
- F Fill
- G Go to memory address, program start
- H Search
- I ASCII-Format
- L Load in memory
- M Memory list
- N Number conversion (only in IDEDOS v.9x)
- O Memory switch
- P Print (only in IDEDOS v.8x)
- R Register (directories)
- T Transfer memory blocks into another memory addresses
- S Save from memory on data mediums
- X Exit
- # Decimal in hexadecimal (0-65535, only in IDEDOS v.8x)
- $ Hexadecimal in decimal ($0000-$FFFF, only in IDEDOS v.8x)
- @ Floppy commands
- *r Read track from floppy disk (only in IDEDOS v.8x)
- *w Write track on floppy disk (only in IDEDOS v.8x)
Screenshots[edit | edit source]
-
The CMOS setup of IDE64
-
The boot screen of IDE64 V3.4
-
The menu of CFSFDISK in IDEDOS v9.x
-
...after formatting a new partition
Links[edit | edit source]
| Wikipedia: IDE64 |
- The IDE Project, accessed 31 December 2013
- IDEDOS Project Page, accessed 31 December 2013
- IDE64 Warez Site, access 31 December 2013
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ IDE64 Interface Cartridge User's Guide, accessed 31 December 2013
- ↑ IDE64 v4.1 Hardware Schematic, accessed 1 January 2014



