COS
| BASIC keyword | |
| Keyword: | COS |
| Abbreviation: | - |
| Type: | Function |
| Token code: | 190/$BE |
| Handling routine in BASIC ROM: |
57956–57962 $E264–E26A |
| List of all BASIC keywords | |
Remark: This article describes the BASIC command COS in BASIC V2 of the Commodore 64.
|
Type: Numeric Function |
The numeric function COS is a mathematical function which evaluates to the cosine for a given angle, a number considered to be in radians.
If the term given in the parentheses is non-numerical, the BASIC error ?TYPE MISMATCH ERROR occurs. If the argument expression is not in the range of a floating point value the execution yields the BASIC error ?OVERFLOW ERROR. Omitting the numeric argument or providing to many arguments results in a ?SYNTAX ERROR.
Implementation details[edit | edit source]
A mere seven bytes long, the handling routine in ROM is situated immediately before the much larger (73 bytes) handling routine for SIN: It exploits the mathematical identity which states that
- cos x = sin(x+π/2)
The COS handling routine points to the floating point constant of π/2 (stored at 58080/$E2E0), then adds this figure to whatever argument is held in FAC, before falling through to the SIN handling routine.
Accuracy[edit | edit source]
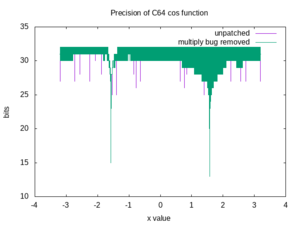
The graph to the right was obtained by comparing results from the BASIC COS function to values computed on a modern x86-type PC.
Where the value of COS is far from zero, that is, for X far from an odd multiple of π/2, COS matches the true value to 29 bits.
COS falls through to SIN, which calls POLY1, which calls MLTPLY ($BA59), and consequently the multiply bug affects its results. A small number of input values give results that match to only 24 bits.
Accuracy degrades for X close to an odd multiple of π/2. This is because the polynomial coefficients are not (and cannot be) exact.
The errors are not symmetric about X == 0; that is, COS(X) is not exactly equal to COS(-X). A few lines of BASIC confirm this discrepancy:
10 XP = COS(0.9) 20 XM = COS(-0.9) 30 PRINT XP - XM
The reported value is -6.98491931E-10, which is 3 * 2-32.
Examples[edit | edit source]
PRINT COS(0)
Output: 1
?COS(23*π/180) (cos of 23 degrees)
Output: .920504854
ABS | AND | ASC | ATN | CHR$ | CLOSE | CLR | CMD | CONT | COS | DATA | DEF | DIM | END | EXP | FN | FOR | FRE | GET | GET# | GOSUB | GOTO | IF | INPUT | INPUT# | INT | LEFT$ | LEN | LET | LIST | LOAD | LOG | MID$ | NEW | NEXT | NOT | ON | OPEN | OR | PEEK | π | POKE | POS | PRINT | PRINT# | READ | REM | RESTORE | RETURN | RIGHT$ | RND | RUN | SAVE | SGN | SIN | SPC | SQR | STATUS/ST | STEP | STOP | STR$ | SYS | TAB | TAN | THEN | TIME/TI | TIME$/TI$ | TO | USR | VAL | VERIFY | WAIT