ADC $hhll
From C64-Wiki
Jump to navigationJump to search
| Mnemonic: | ADC $hhll | ||||||
| 2. Schreibweise: | {{{2. Schreibweise}}} | ||||||
| Opcode: | $6D | ||||||
| Operator(en): | $ll $hh | ||||||
| Byte count: | 3 | ||||||
| Command type: | Arithmetic- and logic command | ||||||
| Address mode: | absolute | ||||||
| register flags: | |||||||
| Carry Flag | |||||||
| Negative Flag | |||||||
| Overflow Flag | |||||||
| Zero Flag | |||||||
| Cycles: | 4 | ||||||
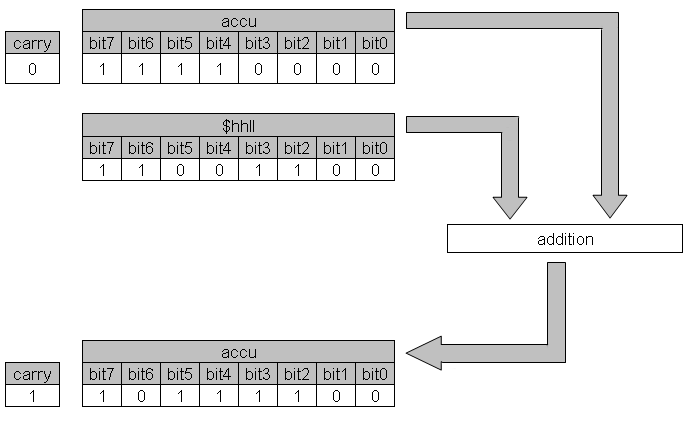
The assembler command ADC $hhll adds the content of memory location $hhll to the accumulator.
If the carry flag is set the result is incremented by one.
Therefore the carry flag should be cleared with CLC before an addition; unless the behaviour is intended.
The result is stored in the accumulator.
If the result is bigger than 255 ($ff) the carry flag is set to be used in multibyte addition as the carry from one byte to the next higher byte. If the carry flag is set in single-byte arithmetic or after the highest order byte has been processed in multi-byte arithmetic, then it should be treated as an overflow.
Function flow
Explanation of the mnemonic shortcut
| ADC | ADd with Carry |
| Add accumulator with operator and carry flag |
Example
; This program adds two 16 bit numbers
; and displays the result on the screen.
; Start program with SYS 49152
*=$c000 ; start address of the program
AXOUT = $bdcd
start clc ; clear carry bit
lda l_num1 ; low byte of 1st number
adc l_num2 ; add low byte of 2nd number
sta l_result ; store low byte in result
lda h_num1 ; high byte of 1st number
adc h_num2 ; add high byte of 2nd number
sta h_result ; store high byte in result
ldx l_result ; low byte of result in X register
lda h_result ; high byte of result in accumulator
jsr AXOUT ; display 16 bit number
rts ; return to BASIC
l_num1 .byte $00 ; number 1 = $1000
h_num1 .byte $10
l_num2 .byte $55 ; number 2 = $2155
h_num2 .byte $21
l_result .byte $00 ; result = $0000
h_result .byte $00
.c000 18 clc .c001 ad 1d c0 lda $c01d .c004 6d 1f c0 adc $c01f .c007 8d 21 c0 sta $c021 .c00a ad 1e c0 lda $c01e .c00d 6d 20 c0 adc $c020 .c010 8d 22 c0 sta $c022 .c013 ae 21 c0 ldx $c021 .c016 ad 22 c0 lda $c022 .c019 20 cd bd jsr $bdcd .c01c 60 rts >c01d 00 >c01e 10 >c01f 55 >c020 21 >c021 00 >c022 00
Comparison of the example program with BASIC
10 Z1=4096 : REM $1000 (4096) 20 Z2=8533 : REM $2155 (8533) 30 E=Z1+Z2 40 PRINT E : REM $3155 (12629)